The Complementary Anti-Parallel Double-Helix Linked-List

The entire behaviour, structure and characteristics of DNA (and RNA) are determined by the way in which its constituent chemical molecules interact and bond with each other
DNA and RNA are essentially Linked Lists1 of base-pairs
How this was established by pioneers Watson & Crick, etc, is detailed in Research Work Stream 00
On this page, we will be looking at some fundamental aspects of DNA’s structure…
“The first essentially correct three-dimensional structure of the DNA molecule was proposed in 1953 by James Watson and Francis Crick at Cambridge University. The structure was dazzling in its elegance and revolutionary in suggesting how DNA duplicates itself, controls hereditary traits, and undergoes mutation” (Hartl 2020, p. 7)
“In the Watson–Crick structure, DNA consists of two long chains of subunits [or ‘rungs’] twisted around one another to form a double-stranded helix. The double helix is right-handed, which means that as one looks along the barrel, each chain follows a clockwise path as it progresses” (Hartl 2020, p. 7)
Complementary Base Pairing
“The subunits (or ‘rungs’) of each strand are nucleotides, each of which contains any one of four chemical constituents called bases. The four bases in DNA are:”
“Adenine (A)” “Guanine (G)” “Thymine (T)” “Cytosine (C)” (Hartl 2020, p. 7)
“This principle explains how only four bases in DNA can code for the huge amount of information needed to make an organism. It is the linear order or sequence of bases along the DNA that encodes the genetic information, and the sequence is completely unrestricted. The complementary pairing is also called Watson–Crick base pairing” (Hartl 2020, p. 8)
“Each DNA strand has a polarity, or directionality, like a chain of circus elephants linked trunk to tail. In this analogy, each elephant corresponds to one nucleotide along the DNA strand. The polarity is determined by the direction in which the nucleotides are pointing. The “trunk” end of the strand is called the 5’ end of the strand, and the “tail” end is called the 3’ end. In double-stranded DNA, the paired strands are oriented in opposite directions: The 5’ end of one strand is aligned with the 3’ end of the other. The oppositely oriented strands are said to be antiparallel”
(Hartl 2020, p. 8)
The Key DNA Structure
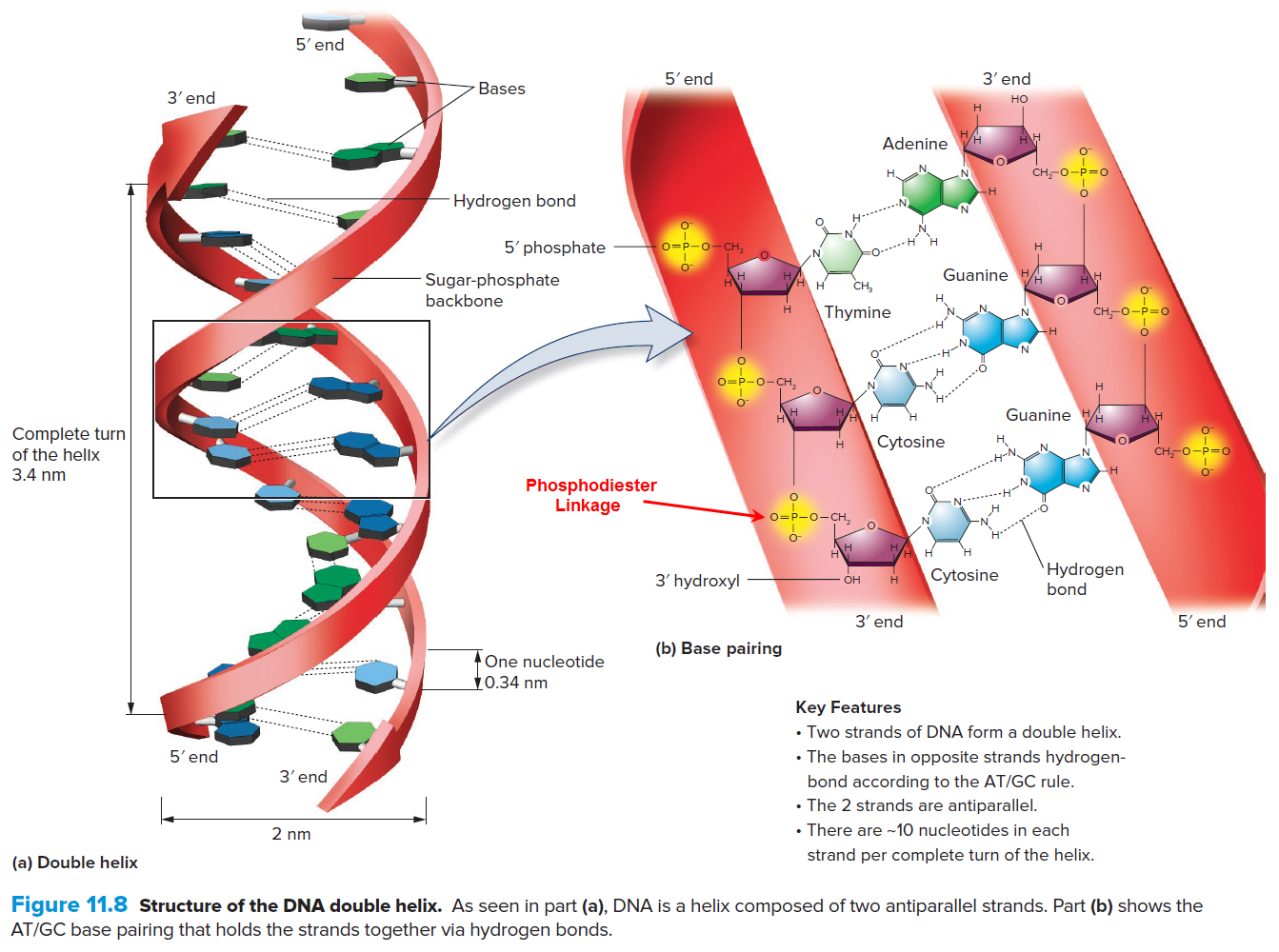
Image: Based on (Brooker et al. 2020, p. 219) Figure 11.8 Mark-up in RED by David Husband
In the image above the Phosphodiester Bonds are highlighted in YELLOW and one of them is pointed out…
The Phosphodiester Bonds (Linkages)
DNA and RNA are essentially Linked Lists1 of base-pairs with the chemical linkages between base-pairs being achieved by Phosphodiester Bonds
Discussed in more detail here
Important page !!
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sense_(molecular_biology)
References:
Hartl, D. L., 2020. Essential Genetics and Genomics. JONES & BARTLETT PUB INC.
Weaver, R., 2012. Molecular biology. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Brooker, R. J., Widmaier, E. P., Graham, L. E. and Stiling, P. D., 2020. Biology. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education.
In Computer Science, a Linked-List is a fundamental data-structure. In Forth, a Linked-List containing Threaded Code is the essence of Forth’s Dictionary ↩ ↩2
